Unleashing the Power of Medieval War Machines
Welcome to the world of medieval warfare, where armies clashed on vast battlefields and employed various war machines to gain the upper hand. In this section, we will introduce you to the fascinating realm of medieval warfare and the critical role that war machines played in shaping the outcome of battles.
Introduction to Medieval Warfare
Medieval warfare was characterized by intense battles fought between kingdoms and empires during the Middle Ages. These conflicts often involved sieges, where one side would lay siege to a fortified city or castle, seeking to breach its defenses and conquer it. The development and utilization of war machines became crucial in these sieges, as they provided the means to overcome the formidable fortifications of the enemy.
From massive catapults to towering siege towers, medieval war machines were designed to unleash destruction upon enemy strongholds and break through their defenses. These formidable machines were feats of engineering and ingenuity, representing the pinnacle of military technology during the Middle Ages.
The Role of War Machines in Medieval Military
War machines played a pivotal role in medieval military strategies. They were employed to assault fortified positions, breach walls, and create chaos within the enemy’s ranks. These machines were capable of hurling projectiles, battering down barriers, and providing tactical advantages to the attacking forces.
One of the primary purposes of war machines was to instill fear and demoralize the defending forces. The sight and sound of massive projectiles soaring through the air or the relentless pounding of a battering ram against a fortress gate struck terror into the hearts of the defenders. This psychological warfare aspect of war machines often contributed to the surrender or collapse of the enemy’s defenses.
War machines also offered strategic advantages by providing a means to overcome the formidable obstacles presented by fortified positions. Siege towers allowed attackers to scale the walls and gain a foothold within the enemy’s defenses, while battering rams were used to break down barriers such as gates or portcullises. These machines provided a means to breach the fortifications and pave the way for the main assault.
Understanding the significance of war machines in medieval warfare provides valuable insights into the dynamics and challenges faced by armies during that era. To delve deeper into the intriguing world of medieval military, you may want to explore topics such as medieval military hierarchy, medieval military tactics, and medieval battle formations.
Now that we have established the importance of war machines in medieval warfare, let’s explore some specific types of war machines, such as catapults, trebuchets, siege towers, and battering rams, in the following sections.
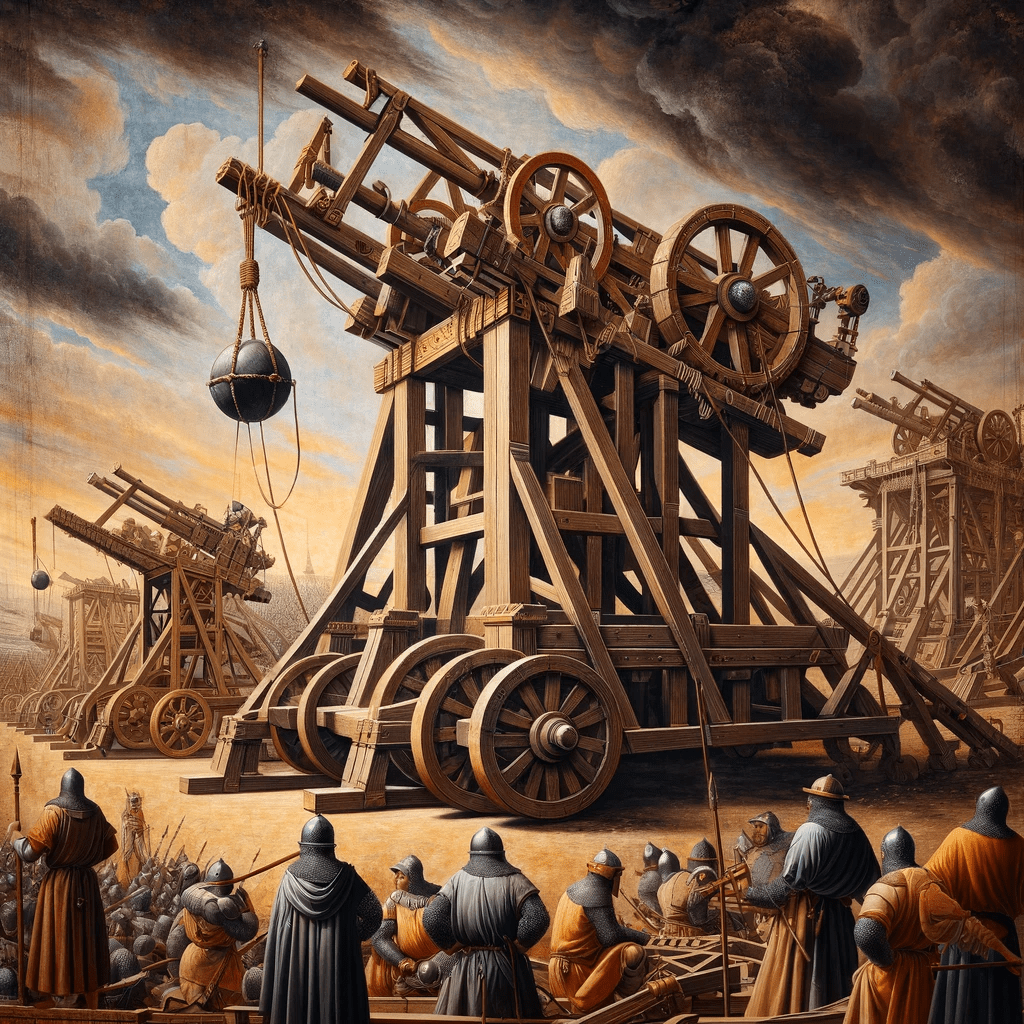
Catapults and Trebuchets
In the realm of medieval warfare, catapults and trebuchets were formidable war machines that played a pivotal role in sieges and battles. These powerful devices were capable of launching projectiles with incredible force, wreaking havoc on enemy defenses.
Catapults: Hurling Destruction
Catapults were designed to hurl various projectiles, such as stones, rocks, and even flaming objects, towards enemy fortifications. These siege engines utilized tension or torsion to store energy and release it rapidly, propelling the projectiles towards their targets.
The range and destructive power of catapults made them invaluable in siege warfare. They were used to breach walls, destroy towers, and demoralize the defenders. The sheer force unleashed by catapults could turn the tide of a battle, creating chaos and confusion among the enemy ranks.
| Catapult Type | Range | Projectile Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Mangonel | 150 – 300 yards | 20 – 50 pounds |
| Ballista | 300 – 400 yards | 5 – 30 pounds |
Trebuchets: The Mighty Counterweight
Trebuchets, on the other hand, were larger and more complex war machines than catapults. These massive devices relied on a counterweight system to launch projectiles with astonishing accuracy and power. Trebuchets were capable of hurling large stones, barrels filled with projectiles, or even diseased animals into enemy territory.
The trebuchet’s design allowed it to generate tremendous force, making it an effective weapon for both breaking down fortifications and engaging enemy troops. Its ability to launch projectiles over long distances gave it a strategic advantage in siege warfare.
| Trebuchet Type | Range | Projectile Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Traction Trebuchet | 150 – 300 yards | 50 – 200 pounds |
| Counterweight Trebuchet | 300 – 400 yards | 100 – 500 pounds |
These powerful medieval war machines, the catapults and trebuchets, were instrumental in shaping the outcomes of battles and sieges. Their ability to launch projectiles with great force and precision struck fear into the hearts of their adversaries.
To learn more about medieval warfare, including the medieval military hierarchy, medieval military tactics, and medieval battle formations, be sure to check out our related articles. Understanding the strategies and equipment used in medieval times can provide fascinating insights into the rich tapestry of history.
Siege Towers and Battering Rams
In the realm of medieval warfare, siege towers and battering rams were two prominent war machines utilized to breach fortified defenses. These powerful instruments played a crucial role in sieges and castle assaults, allowing armies to overcome formidable obstacles and conquer enemy strongholds.
Siege Towers: Scaling the Walls
Siege towers were towering structures specifically designed to aid in breaching castle walls. These colossal wooden structures, often resembling multi-story towers, provided a means for attackers to approach and scale the walls while providing cover and protection.
Equipped with ladders or ramps, siege towers allowed soldiers to ascend to the same height as the castle walls, enabling them to engage in close combat with defenders. The towers were often equipped with archers and other ranged units, who could rain down arrows and projectiles upon the defenders, weakening their resistance.
To further enhance their functionality, some siege towers were equipped with drawbridges or large platforms at the top. These platforms allowed soldiers to advance onto the walls, establishing a foothold for further assault. By utilizing siege towers, attacking forces could overcome the vertical advantage of defenders and gain access to the inner parts of the castle.
Battering Rams: Breaking Barriers
Another formidable war machine employed during medieval warfare was the battering ram. These devices were specifically designed to break through defensive barriers, such as castle gates and doors. Consisting of a large, heavy beam with a protective cover, battering rams were operated by a group of soldiers who would repeatedly strike the target with forceful blows.
The effectiveness of battering rams relied on their ability to generate enough impact and force to overcome the strength of the defensive structures. The ramming motion, executed by the soldiers pushing or pulling the beam, aimed to weaken or break down the barriers, providing an entry point for attacking forces.
Battering rams were often accompanied by additional protective elements, such as mobile shelters or shed-like structures, to shield the soldiers from projectiles launched by defenders. This allowed the attackers to focus on their task without being hindered by defensive counterattacks.
Using siege towers and battering rams, medieval armies could breach the fortifications of enemy castles and strongholds, ultimately gaining the upper hand in sieges. These war machines, along with other medieval military tactics and battle formations, formed a crucial part of medieval warfare, shaping the outcome of numerous conflicts throughout history.
For more information on medieval military strategies, tactics, and the hierarchy within medieval armies, check out our articles on medieval military hierarchy, medieval military tactics, and medieval battle formations.
War Wagons and Traction Trebuchets
In the realm of medieval war machines, two formidable contraptions stand out: war wagons and traction trebuchets. These machines played a crucial role in medieval warfare, offering unique advantages on the battlefield.
War Wagons: Mobile Fortresses
War wagons were essentially mobile fortresses, designed to provide protection to troops during sieges and battles. These massive wheeled structures were equipped with various defensive features, such as walls, towers, and even makeshift ramparts. War wagons were built to withstand enemy attacks while allowing soldiers to maneuver and engage in combat.
War wagons offered several advantages on the battlefield. They provided a secure vantage point for archers and other ranged attackers, allowing them to rain down arrows and other projectiles on the enemy from a protected position. Additionally, war wagons could be used to transport troops, supplies, and even heavy weaponry to strategic locations, making them a versatile asset in medieval warfare.
Let’s take a look at some key features of war wagons:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Defensive Walls | Thick wooden walls provided protection from enemy projectiles and assaults. |
| Towers | Elevated towers on the war wagons allowed archers and soldiers to have a clear line of sight and attack from above. |
| Ramparts | Some war wagons had makeshift ramparts that provided additional cover for troops. |
| Mobility | War wagons were designed with wheels, enabling them to be maneuvered across the battlefield. |
Traction Trebuchets: Portable Powerhouses
Traction trebuchets were powerful siege weapons that could launch heavy projectiles over long distances. Unlike traditional trebuchets that relied on a counterweight system, traction trebuchets used human or animal power to generate the force needed to hurl objects at enemy fortifications.
These trebuchets were known for their portability and ease of assembly, making them a preferred choice for medieval armies on the move. Traction trebuchets could be disassembled and transported to different locations, allowing for flexibility in siege tactics.
Here are some notable features of traction trebuchets:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Human or Animal Power | Traction trebuchets were operated by teams of soldiers or animals, such as horses or oxen, pulling ropes to create the necessary force. |
| Projectiles | These trebuchets could launch a variety of projectiles, including stones, flaming projectiles, and even diseased animals or corpses. |
| Portability | Traction trebuchets were designed to be quickly assembled and disassembled, enabling armies to transport them to different locations as needed. |
| Range and Power | Traction trebuchets were capable of launching projectiles at impressive distances, inflicting substantial damage to enemy fortifications. |
War wagons and traction trebuchets were key players in medieval warfare, each offering distinct advantages on the battlefield. Whether it was the mobile fortresses providing protection and mobility or the portable powerhouses launching devastating projectiles, these war machines played a significant role in shaping medieval military tactics and strategies.
To learn more about medieval warfare and other aspects of the medieval world, check out our articles on medieval military hierarchy, medieval military tactics, and medieval battle formations.
Mangonels and Ballistae
In the realm of medieval war machines, two formidable weapons stand out: mangonels and ballistae. These siege engines played a crucial role in medieval warfare, allowing armies to launch projectiles with precision and devastating force.
Mangonels: Launching Projectiles
Mangonels were powerful artillery machines used to launch various projectiles at enemy fortifications. These war machines relied on tension and torsion to propel their ammunition. The mangonel’s arm, often made of wood, would be tightly twisted with ropes or sinews. When released, the stored energy would unleash a powerful launch, hurling rocks, stones, or other projectiles towards the enemy.
The range and impact of mangonels varied depending on their size and design. Smaller mangonels, known as “onagers,” were highly maneuverable and capable of launching projectiles up to 400 meters away. Larger mangonels, like the “perrier,” could launch heavier projectiles, such as stone balls, with devastating force. These siege engines were a force to be reckoned with, capable of breaching castle walls and causing significant damage to fortifications.
Ballistae: Precision Power
Ballistae, another fearsome war machine, were renowned for their precision and power. These crossbow-like devices utilized torsion to launch large bolts or arrows at high speeds. Unlike regular crossbows, ballistae were much larger and required a team of soldiers to operate effectively.
The ballista consisted of a frame with a central beam, known as the “slider,” which could move back and forth. Attached to the slider was a pair of arms with twisted skeins or rope springs. These springs, when released, would unleash tremendous force and propel the bolt or arrow towards the target.
Ballistae were highly accurate and could pierce heavy armor or penetrate castle walls. They were often employed to target high-value enemy personnel or to weaken fortifications during sieges. The power and precision of ballistae made them a formidable weapon of choice for medieval armies.
To gain a deeper understanding of medieval warfare, it’s essential to explore the various war machines that shaped battles and sieges. Mangonels and ballistae were just two of the many innovative technologies employed during this period. By harnessing the power of these mighty machines, medieval armies were able to change the course of history. For more information on medieval military strategies and tactics, visit our article on medieval military tactics.
The Impact of Medieval War Machines
Medieval war machines were not only formidable in terms of their destructive capabilities but also had a significant impact on the battlefield. Let’s explore two key aspects of their impact: psychological warfare and strategic advantages and limitations.
Psychological Warfare
Medieval war machines, with their towering structures and devastating power, had a profound psychological impact on both defenders and attackers. Imagine being part of a defending army, witnessing massive catapults hurling projectiles towards your walls or trebuchets launching boulders that could demolish your fortifications. The sheer sight and sound of these war machines instilled fear and intimidation, often demoralizing the defenders and weakening their resolve.
On the other hand, as an attacking force, utilizing war machines could help create a sense of terror and panic among the defenders. The anticipation and uncertainty of when and where the next projectile would strike created an atmosphere of psychological distress, making it challenging for the defenders to maintain their composure.
Strategic Advantages and Limitations
While medieval war machines provided strategic advantages, they also had their limitations. One of the main advantages was their ability to breach walls and fortifications, enabling attackers to gain access to heavily defended areas. Siege towers, for example, allowed troops to scale walls and engage in close combat with the defenders. Battering rams were effective in breaking through gates and barriers, providing access for the attacking forces.
However, war machines also had their limitations. They were often slow and cumbersome, requiring significant time and resources to construct and transport to the battlefield. Their size and weight made them vulnerable to defensive countermeasures, such as projectiles launched from the walls or defensive structures designed to impede their progress.
Moreover, the effectiveness of war machines relied heavily on favorable terrain and weather conditions. Factors such as wind direction, rain, or rough terrain could impact their accuracy and range, reducing their overall effectiveness in battle. Additionally, the cost and maintenance required for war machines were substantial, making them inaccessible to smaller armies or less wealthy factions.
Understanding the impact of medieval war machines, both from a psychological and strategic standpoint, provides insight into the dynamics of medieval warfare. Combining these war machines with medieval military tactics and deploying them within medieval battle formations, commanders sought to gain a significant advantage on the battlefield. The hierarchy and organization of the medieval military played a critical role in effectively utilizing war machines to achieve their objectives.
