In the medieval times, the guild system served as a crucial foundation for the flourishing commerce of the era. Understanding the medieval guilds and their importance in medieval society provides valuable insights into the economic landscape of the time.
Understanding the Medieval Guilds
Medieval guilds were formal associations of craftsmen and merchants, organized to protect their interests, regulate trade, and maintain high standards of craftsmanship. These guilds played a pivotal role in shaping the medieval economy by bringing together individuals with similar skills and trades.
Medieval guilds were often established in cities and towns, where economic activities thrived. They encompassed various types of guilds, including merchant guilds that focused on trade and craft guilds that specialized in specific crafts or industries. Each guild had its own set of rules, regulations, and hierarchies.
To delve deeper into the world of medieval guilds, you can explore our comprehensive article on medieval guilds.
Importance of Guilds in Medieval Society
The guilds held immense importance in medieval society and were highly regarded for their contributions. They served as more than just trade organizations; they were integral parts of the social fabric.
Guilds provided a sense of belonging, camaraderie, and support to their members. They offered a platform for craftsmen and merchants to share knowledge, exchange ideas, and pass down their skills through apprenticeships. The guilds also played a significant role in the regulation of trade, ensuring fair practices, quality control, and the protection of consumers.
By establishing strict standards and regulations, guilds helped maintain the reputation and integrity of their respective crafts. They maintained a watchful eye on the quality of products, the training of apprentices, and the conduct of their members. This commitment to excellence contributed to the overall growth and development of medieval commerce.
To gain a deeper understanding of the structure and organization of guilds, you can explore our article on medieval guild hierarchy and medieval guild apprenticeship.
The medieval guilds left a lasting legacy on the economic and social landscapes of the time. Their influence on trade, craftsmanship, and the development of medieval society cannot be understated. By exploring the origins, roles, and impact of guilds, we can gain a greater appreciation for the intricate and interconnected nature of medieval commerce.
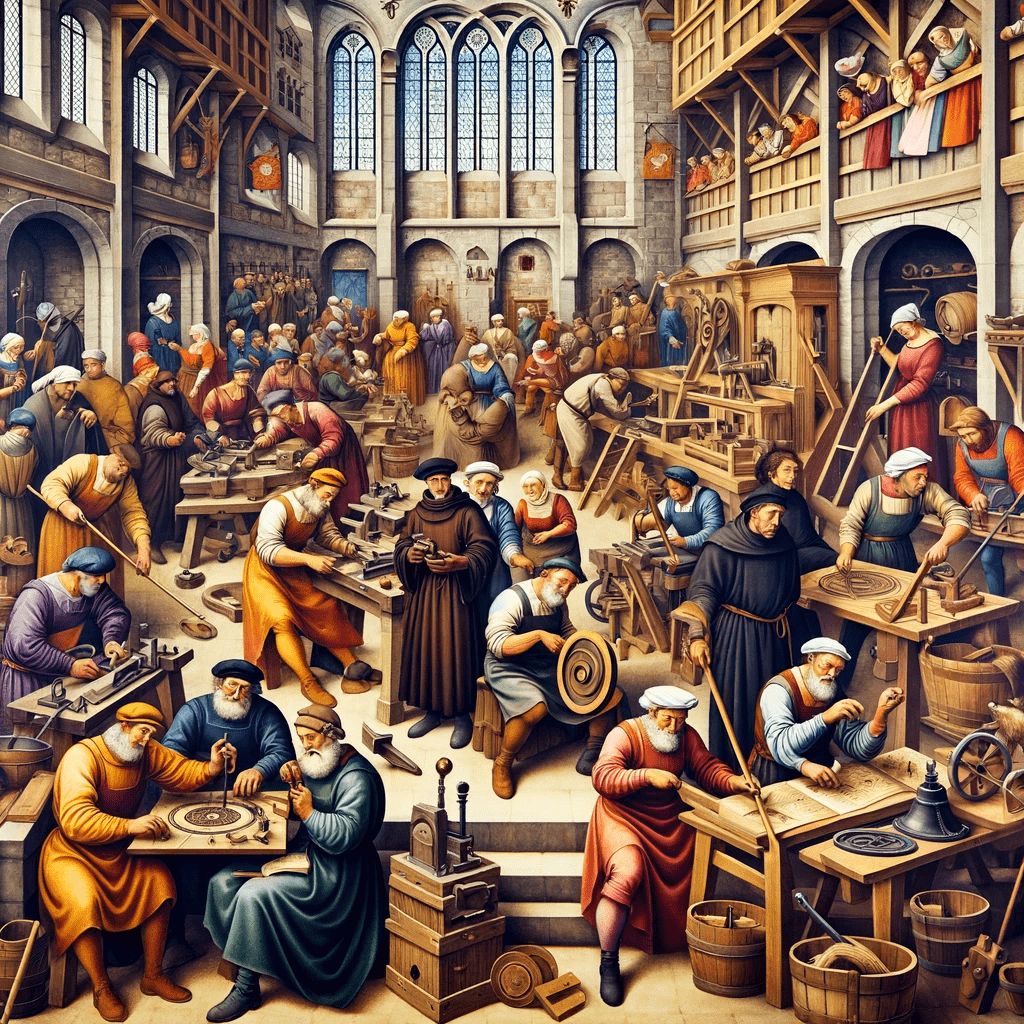
The Origins of Guilds
In order to truly understand the medieval guild system, it is important to explore its origins and how it evolved over time. The guilds of the Middle Ages played a significant role in shaping the economic landscape of that era.
Early Guilds and Trade Associations
The concept of guilds can be traced back to early civilizations, where groups of craftsmen and merchants formed associations to protect their interests and ensure fair trade practices. These early guilds were often centered around specific trades or crafts, such as metalworking or weaving.
In medieval times, these trade associations grew in prominence and became more structured. They provided a platform for artisans and merchants to come together, share knowledge, and protect their common interests. The guilds were not only responsible for regulating the trade and craftmanship but also played a crucial role in maintaining quality standards, ensuring fair pricing, and protecting the rights of their members.
Evolution of Guilds in Medieval Times
As medieval society developed, so did the guild system. Guilds became more organized and began to exert significant influence over commerce and trade. They established rules and regulations that governed their respective industries and provided a framework for apprenticeship and membership.
During the Middle Ages, guilds expanded in numbers and diversity. Various types of guilds emerged, including merchant guilds, craft guilds, and trade guilds. Each type had its own specific focus and function within the economic structure. Merchant guilds, for example, were primarily concerned with the regulation and control of trade, while craft guilds were dedicated to the advancement and protection of specific crafts.
The guilds of medieval Europe played a central role in the economic and social fabric of their respective communities. They not only facilitated economic exchange but also provided a sense of identity and community for their members. To learn more about the significance of guilds in medieval society, visit our article on medieval guilds.
By understanding the origins and evolution of guilds in medieval times, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the impact they had on commerce, craftsmanship, and the development of the medieval middle class. The guild system left a lasting legacy that continues to shape our understanding of medieval society and its economic structure.
Structure and Organization of Guilds
The structure and organization of medieval guilds played a vital role in their functioning and influence. Let’s delve into two key aspects: guild hierarchy and leadership and membership and apprenticeship.
Guild Hierarchy and Leadership
Medieval guilds had a well-defined hierarchical structure that ensured smooth operations and efficient decision-making. At the top of the hierarchy was the guild master, who held significant authority and was responsible for overseeing the guild’s affairs. The guild master was often an experienced and respected member of the craft or trade.
Assisting the guild master were other positions of leadership, such as the wardens or wardmasters. These individuals were responsible for maintaining discipline within the guild and ensuring that members adhered to the established regulations. Wardens also had the task of inspecting the quality of the goods produced by guild members to maintain high standards.
Below the guild master and wardens were the general guild members. They were skilled craftsmen or tradespeople who had completed their apprenticeships and were recognized by the guild as qualified practitioners. The guild members had the privilege of participating in decision-making processes and voting on important matters that concerned the guild.
Membership and Apprenticeship
Membership in a medieval guild was not open to everyone. To become a guild member, individuals had to go through a structured process that typically started with apprenticeship. Aspiring craftsmen or tradespeople would enter into an apprenticeship with a skilled guild member, known as a master craftsman. During the apprenticeship, which often lasted several years, the apprentice would learn the craft or trade under the guidance of the master craftsman.
Upon completing the apprenticeship, the apprentice would become a journeyman. As a journeyman, they were allowed to work independently and earn wages. However, they were still under the supervision of the guild and had to adhere to its regulations. Journeymen had the opportunity to improve their skills and gain experience before becoming eligible for full guild membership.
To become a full-fledged guild member, a journeyman had to submit a masterpiece or a masterpiece, showcasing their mastery of the craft. The masterpiece was evaluated by the guild and, if deemed satisfactory, the journeyman would be admitted as a guild member. Once a member, they enjoyed the privileges and protections of the guild, including access to guild resources, support, and representation.
The structured membership and apprenticeship system ensured that guilds maintained high standards of craftsmanship and regulated the entry of practitioners into the trade or craft. This system also facilitated the transfer of knowledge and skills from experienced guild members to the next generation.
Understanding the structure and organization of medieval guilds helps us appreciate the significant role they played in shaping and regulating commerce during that era. To explore more about medieval guilds and their influence, check out our article on medieval guilds.
Roles and Functions of Guilds
Medieval guilds played vital roles in the economic and social fabric of society. Let’s explore two key functions: regulating trade and craftsmanship and setting standards and quality control.
Regulating Trade and Craftsmanship
Guilds had the responsibility of regulating trade and craftsmanship within their respective industries. They served as governing bodies that oversaw the activities of artisans, craftsmen, and merchants. By establishing rules and regulations, guilds aimed to maintain order, protect the interests of their members, and ensure fair competition.
One way guilds regulated trade was through the establishment of trade monopolies. Guilds had the authority to control who could practice a specific trade or craft, limiting the number of individuals allowed to engage in a particular profession. This control over membership helped ensure that only skilled individuals who had completed the necessary training and apprenticeships could operate within the trade. For a detailed look at guild membership and apprenticeship, refer to our article on medieval guild apprenticeship.
Additionally, guilds set rules regarding the quality of goods produced by their members. They established standards and guidelines for the production process, materials used, and finished products. This commitment to maintaining quality not only protected the reputation of the guild but also ensured that consumers received goods of a certain standard. By upholding these regulations, guilds aimed to safeguard the interests of both their members and the general public.
Setting Standards and Quality Control
Another crucial function of guilds was to set standards and enforce quality control measures. Guilds aimed to maintain the excellence of their craft or trade by establishing guidelines for the production of goods. This included specifying the types of materials that should be used, the techniques to be employed, and even the dimensions or specifications of the final products.
To enforce these standards, guilds conducted inspections and assessments of the work produced by their members. This ensured that the goods met the required quality benchmarks before they were offered for sale. By doing so, guilds safeguarded the reputation of their trade and instilled confidence in consumers.
To get a better understanding of the hierarchy and leadership within guilds, refer to our article on medieval guild hierarchy.
Through their role in regulating trade and craftsmanship and setting standards and quality control measures, guilds contributed significantly to the development and growth of medieval commerce. Their influence extended not only to local trade but also to international markets, as guilds played a crucial role in shaping trade routes and establishing trading networks. For more information on the economic impact of guilds, explore our article on medieval guilds in Europe.
The decline of guilds brought about changes in the economic landscape, but their legacy continues to resonate in various aspects of modern society. The guild system laid the foundation for the development of modern trade associations and professional organizations, showcasing the lasting influence of this medieval institution.
Guilds and Economic Influence
During the medieval period, guilds played a significant role in shaping the economic landscape. As economic powerhouses, guilds exerted a profound impact on both local communities and international trade.
Guilds as Economic Powerhouses
Guilds were not just mere associations; they held considerable economic influence. By bringing together skilled craftsmen and merchants, guilds established a system that regulated trade, protected the interests of its members, and ensured the quality of goods and services.
The economic power of guilds stemmed from their ability to control and monopolize certain trades and crafts. Guild members enjoyed exclusive rights to produce and sell specific goods, which allowed them to maintain a level of control over supply and demand. This control enabled guilds to set prices, establish standards, and control the quality of products, thereby ensuring fair competition and consumer satisfaction.
Impact on Local and International Trade
Guilds played a pivotal role in both local and international trade during the medieval period. Locally, guilds facilitated trade within their communities, acting as intermediaries between producers and consumers. They provided a platform for artisans and merchants to connect, ensuring the steady flow of goods and services.
Internationally, guilds had a significant impact on trade routes and commerce. Some guilds specialized in long-distance trading, establishing connections with other guilds in different regions and countries. These connections expanded trade networks and facilitated the exchange of goods and knowledge across borders.
Guilds also influenced trade regulations and policies. They had the power to negotiate with local authorities and secure favorable conditions for their members. In some cases, guilds were granted exemptions from certain taxes or tariffs, further enhancing their economic advantage.
The economic influence of guilds extended beyond trade. They played a vital role in the development of urban centers, contributing to the growth of cities and towns. Guilds promoted economic stability, fostered innovation, and supported the rise of the medieval middle class.
By understanding the impact of guilds as economic powerhouses, we can gain a deeper appreciation for their role in shaping medieval commerce. From local trade regulations to international connections, guilds left an enduring legacy on the economic landscape of the time. To learn more about medieval guilds, their structure, and functions, visit our article on medieval guilds.
Decline and Legacy of Guilds
As time went on, the once thriving medieval guild system began to experience a decline. Various factors contributed to this decline, ultimately leading to the transformation and eventual dissolution of guilds. However, the legacy left by these organizations continued to influence commerce and society for centuries to come.
Factors Leading to the Decline
The decline of guilds can be attributed to several key factors.
1. Changes in Economic Landscape: With the emergence of new economic practices, such as the rise of capitalism and the growth of international trade, the medieval guild system faced challenges. The guilds’ rigid regulations and control over trade and craftsmanship became less compatible with the changing economic landscape.
2. Technological Advancements: The advent of new technologies and industrialization brought about significant changes in production methods. These advancements reduced the need for skilled artisans, as manufacturing processes became more mechanized and efficient. The guilds, which relied heavily on traditional craftsmanship, struggled to adapt to these changes.
3. Political Shifts: Political changes, such as the centralization of power in monarchies and the rise of nation-states, also played a role in the decline of guilds. The guilds, which once held significant influence and autonomy, faced increasing regulation and control from the ruling authorities. This shift in power dynamics weakened the guilds’ ability to maintain their autonomy and protect their interests.
4. Social and Cultural Changes: As society evolved, new social and cultural norms emerged. The guild system, with its hierarchical structure and strict regulations, began to clash with the changing social dynamics. The rise of individualism and the desire for personal freedom undermined the collective nature of guilds, leading to a decline in their influence.
Lasting Influence of the Guild System
Despite their decline, the legacy of guilds persisted long after their dissolution. The guild system left a lasting impact on the economic, social, and cultural fabric of medieval society and beyond.
1. Craftsmanship and Quality Standards: The guilds’ emphasis on maintaining high standards of craftsmanship and quality control set a precedent for future generations. The notion of skilled craftsmanship and the pursuit of excellence in various industries can be traced back to the guild system.
2. Professional Associations and Trade Unions: The guilds served as precursors to modern-day professional associations and trade unions. These organizations carry forward the tradition of protecting the interests of their members and promoting the welfare of their respective industries.
3. Apprenticeship and Education: The guilds’ apprenticeship system paved the way for structured vocational training and education. The concept of passing down knowledge and skills from master to apprentice is still prevalent today, ensuring the continuation of specialized trades and professions.
4. Guild Halls and Symbols: Many guild halls, which once served as meeting places and centers of trade, still stand as architectural reminders of the guild system. Additionally, guild symbols and emblems, such as coats of arms, continue to be used and recognized as historical representations of guilds.
The decline of the medieval guild system marked the end of an era, but its influence remained imprinted on the development of commerce and society. The guilds played a pivotal role in shaping medieval society and laying the groundwork for future economic and social structures. Today, their legacy stands as a testament to the enduring impact of these medieval institutions.
