Unveiling Medieval Armor
In the realm of medieval history, medieval armor holds a significant place. It was an essential aspect of the medieval period, serving as protection for warriors on the battlefield. Let’s delve into the world of medieval armor and explore its importance during those times.
Introduction to Medieval Armor
Medieval armor refers to the protective gear worn by knights and soldiers during the medieval period, which spanned roughly from the 5th to the 15th century. Armor played a crucial role in safeguarding the wearer from the weapons and projectiles used in combat. It provided vital protection against swords, arrows, and other deadly weapons, ensuring the survival of warriors in the heat of battle.
Medieval armor was crafted with great skill and attention to detail. It consisted of various components that covered different parts of the body, including the head, torso, arms, and legs. Each part was designed to provide maximum protection while allowing flexibility and ease of movement. To learn more about the different parts of medieval armor, you can check out our article on medieval armor parts.
Importance of Armor in Medieval Times
During the medieval era, armor held immense significance. It not only protected the wearer but also served as a symbol of status, wealth, and power. The armor a knight wore was often intricately designed and embellished, showcasing the knight’s social standing and the resources invested in their defense. Decorative elements, such as engravings and heraldic symbols, were added to armor to distinguish one knight from another.
Armor also played a crucial role in shaping the tactics and strategies of medieval warfare. The presence of well-armored knights on the battlefield had a psychological impact on their opponents. The sight of a formidable knight in shining armor instilled fear and intimidation, often demoralizing the enemy forces.
Moreover, armor provided a sense of security and confidence to the wearer. It allowed knights to engage in close combat without fearing fatal injuries. The protection offered by armor enabled them to fight with greater agility and bravery, knowing that their lives were safeguarded to a certain extent.
Understanding the history and significance of medieval armor is key to comprehending the medieval period as a whole. By exploring the various armor types and their characteristics, we can gain insights into the craftsmanship, technology, and warfare techniques of that era. So let us now embark on a journey to compare the different types of medieval armor in detail.
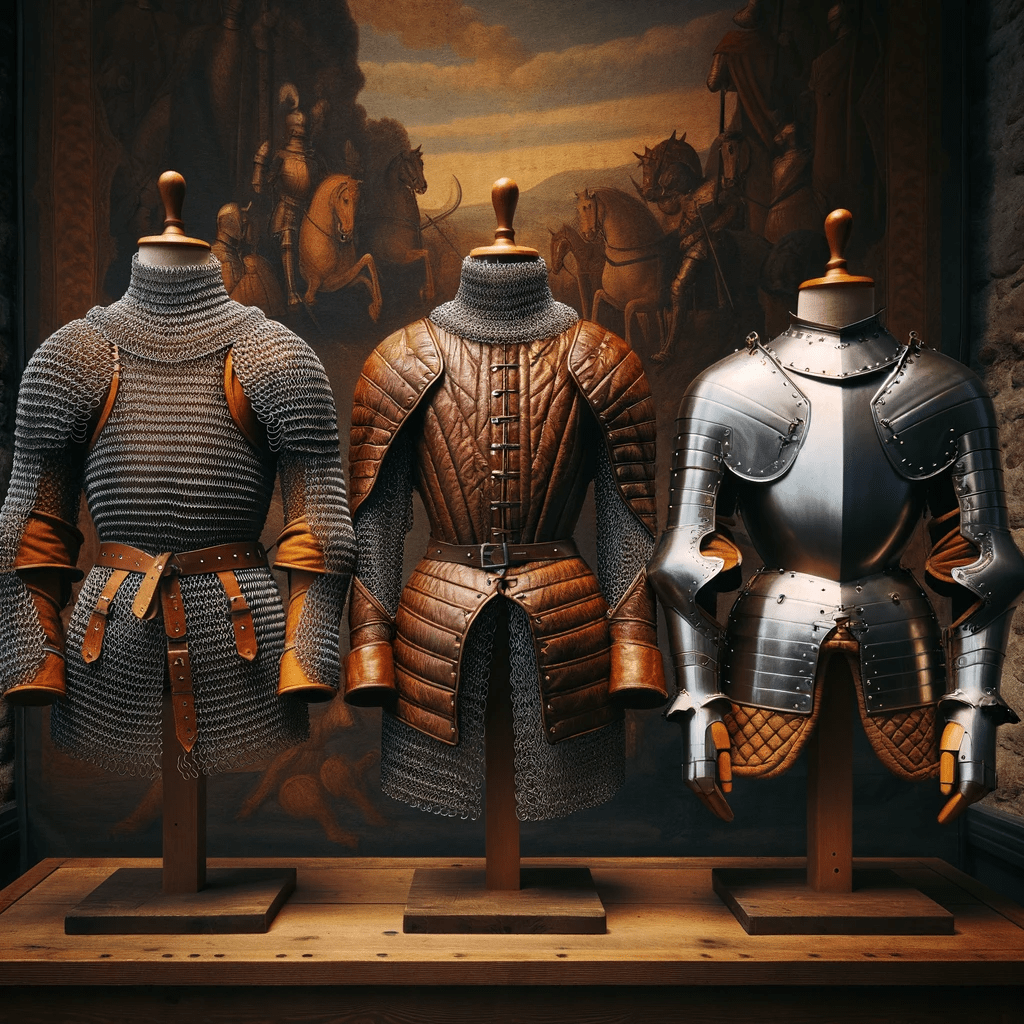
Comparing Armor Types
When exploring the world of medieval armor, you’ll encounter various types that served to protect warriors during battle. Each armor type had its own unique characteristics and provided different levels of protection. Let’s take a closer look at the four main types: chainmail armor, plate armor, lamellar armor, and leather armor.
Chainmail Armor
Chainmail armor is made up of interlocking metal rings, forming a mesh-like garment that covers the body. This armor type offers excellent mobility and flexibility, allowing the wearer to move relatively freely in combat. However, chainmail is less effective against thrusting attacks and can be vulnerable to blunt force trauma. To learn more about the features and characteristics of chainmail armor, refer to our article on medieval armor parts.
Plate Armor
Plate armor consists of metal plates that are meticulously crafted and shaped to fit the body. This armor provides superior protection against both slashing and thrusting attacks. It covers a large surface area, including the chest, back, arms, and legs, offering comprehensive defense on the battlefield. Plate armor, while highly effective, can be heavy and restrict the wearer’s movement to some extent. Discover more about the features and characteristics of plate armor in our article on medieval armor materials.
Lamellar Armor
Lamellar armor is composed of small rectangular plates laced together with cord or leather. This type of armor is known for its flexibility and lightweight nature, allowing for ease of movement during combat. Lamellar armor offers reliable protection against various types of attacks, making it a popular choice among warriors. To delve into the specific features and characteristics of lamellar armor, visit our article on medieval breastplate parts.
Leather Armor
Leather armor is crafted from treated animal hides, providing a combination of protection and flexibility. It was commonly used by foot soldiers and archers due to its light weight and affordability. While leather armor offers limited defense against slashing and piercing weapons, it is more susceptible to damage compared to other armor types. Learn more about the features and characteristics of leather armor in our article on medieval gauntlet parts.
By comparing these different armor types, you can gain a better understanding of their strengths and weaknesses. Each armor type played a significant role during the medieval era, offering protection to warriors on the battlefield. Explore the specific advantages and disadvantages of each armor type in the following sections.
Features and Characteristics
When exploring the different types of medieval armor, it’s important to understand their unique features and characteristics. Let’s take a closer look at the key aspects of chainmail armor, plate armor, lamellar armor, and leather armor.
Chainmail Armor
Chainmail armor, also known as chainmaille or simply mail, is made up of interlocking metal rings. It provides excellent flexibility and protection against cutting and slashing attacks. The rings are typically made of iron or steel, and they come in various sizes and patterns. Chainmail armor was widely used during medieval times due to its effectiveness and relatively lighter weight compared to other armor types.
Some important features of chainmail armor include:
- Flexibility: The interlocking rings allow for a wide range of movement, providing the wearer with flexibility during combat.
- Coverage: Chainmail armor covers the entire body, including the torso, arms, and legs.
- Ring Patterns: Different patterns, such as 4-in-1 or 6-in-1, affect the level of protection and flexibility.
- Padding: Chainmail is often worn over a padded garment, such as a gambeson, to provide additional protection and comfort.
Plate Armor
Plate armor is a type of armor composed of individual metal plates that are strategically shaped and fitted together. These plates offer superior protection against piercing and blunt force attacks. Plate armor is typically made of steel and provides comprehensive coverage to the wearer.
The key features of plate armor include:
- Protection: Plate armor covers the entire body, including the torso, arms, legs, and sometimes the head with a separate helmet.
- Articulation: The plates are joined together with rivets or straps, allowing for flexibility and a range of motion.
- Customization: Plate armor can be tailored to fit the wearer’s body, providing a personalized and snug fit.
- Weight: Plate armor can be heavy, but the weight is distributed across the body, minimizing strain on specific areas.
Lamellar Armor
Lamellar armor consists of small rectangular or polygonal plates, known as lamellae, that are laced together with cords or leather straps. This type of armor offers good protection while also providing flexibility and ease of movement. Lamellar armor was commonly used in various regions, including Asia and Europe, during the medieval period.
The notable features of lamellar armor are:
- Lamellae: The individual plates, made of materials like metal, leather, or horn, are laced together in overlapping rows.
- Versatility: Lamellar armor can be adjusted and customized easily to fit different body shapes.
- Lightweight: Compared to plate armor, lamellar armor is relatively lighter, allowing for increased mobility on the battlefield.
Leather Armor
Leather armor is made from hardened and treated animal hides. Although it provides less protection compared to other armor types, leather armor offers flexibility and agility to the wearer. Leather armor was commonly worn by archers, scouts, and lighter infantry during medieval times.
Key features of leather armor include:
- Flexibility: Leather armor allows for a wide range of movement, making it suitable for agile combat styles.
- Customization: Leather armor can be tailored to fit the wearer’s body shape and size.
- Lightweight: Leather armor is lighter than other types of armor, providing increased mobility and comfort.
Understanding the features and characteristics of different medieval armor types allows you to appreciate their design and functionality. Each type served a specific purpose and offered varying levels of protection on the battlefield. For more information on the different parts and components of medieval armor, refer to our article on medieval armor parts.
Advantages and Disadvantages
When comparing different types of medieval armor, it’s important to consider the advantages and disadvantages of each. Each type of armor had its own strengths and weaknesses, which affected its effectiveness on the battlefield. Let’s explore the advantages and disadvantages of chainmail armor, plate armor, lamellar armor, and leather armor.
Chainmail Armor
Advantages:
- Provides good flexibility and freedom of movement.
- Offers reasonable protection against slashing attacks.
- Allows for good air circulation, minimizing discomfort in hot climates.
- Can be repaired easily by replacing damaged links.
Disadvantages:
- Less effective against piercing attacks, such as arrows or thrusts.
- Limited protection against blunt force trauma.
- Heavy and can cause fatigue over extended periods.
- Vulnerable to rust and corrosion if not properly maintained.
Plate Armor
Advantages:
- Offers excellent protection against both slashing and piercing attacks.
- Provides superior defense against blunt force trauma.
- Distributes the weight evenly across the body, minimizing fatigue.
- Can be customized and fitted to the wearer for optimal protection.
Disadvantages:
- Restricted mobility, especially in the joints.
- Requires assistance to put on and take off.
- Can be expensive and time-consuming to produce.
- Susceptible to denting and damage from heavy blows.
Lamellar Armor
Advantages:
- Provides good protection against slashing and piercing attacks.
- Offers flexibility and freedom of movement.
- Lighter and more comfortable compared to some other armor types.
- Can be adjusted to fit different body shapes.
Disadvantages:
- Vulnerable to thrusting attacks, especially in the gaps between plates.
- Requires regular maintenance to prevent rust and deterioration.
- Can be time-consuming to assemble and disassemble.
- Less protection against blunt force trauma compared to plate armor.
Leather Armor
Advantages:
- Lightweight and allows for greater mobility.
- Provides reasonable protection against slashing attacks.
- Easier to repair compared to other armor types.
- Can be more affordable and accessible for common soldiers.
Disadvantages:
- Limited protection against piercing and blunt force attacks.
- Susceptible to wear and tear over time.
- Requires regular maintenance to prevent drying and cracking.
- Less effective against heavy weapons and armor-piercing projectiles.
Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each type of armor is crucial to grasp their effectiveness and limitations in battle. The choice of armor would often depend on the specific needs and resources of the wearer. To learn more about medieval armor, including its various parts and materials, visit our article on medieval armor parts.
In the next section, we will explore the role and significance of chainmail, plate, lamellar, and leather armor in the history of medieval warfare. Stay tuned to delve deeper into the fascinating world of medieval armor!
Role and Significance in History
Throughout history, various types of armor played a crucial role in protecting warriors on the battlefield. Let’s explore the role and significance of chainmail armor, plate armor, lamellar armor, and leather armor in different historical contexts.
Chainmail Armor
Chainmail armor was widely used during the medieval period, offering excellent protection and flexibility. It consisted of interlocking metal rings, forming a mesh-like structure. Chainmail armor provided effective defense against slashing attacks, although it was less effective against thrusting weapons. Despite its relatively heavy weight, chainmail was popular among knights and infantry due to its ability to distribute the force of impact across a large area. Learn more about the various parts of chainmail armor in our article on medieval armor parts.
Plate Armor
Plate armor, also known as plate mail or full plate armor, emerged in the late medieval period. It was a revolutionary development in the field of armor, offering superior protection against a variety of attacks. Plate armor consisted of metal plates joined together with rivets or straps, covering the entire body. This type of armor provided excellent protection against both slashing and thrusting weapons, making it a preferred choice for knights and nobles. Discover the different parts that make up plate armor in our article on medieval armor parts.
Lamellar Armor
Lamellar armor originated in various regions, including East Asia and Eastern Europe. It consisted of small rectangular or polygonal plates, often made of metal or hardened leather, laced together in overlapping rows. Lamellar armor offered good protection and flexibility, allowing for ease of movement on the battlefield. Its design provided effective defense against slashing attacks, while still maintaining a relatively lightweight compared to plate armor. Although less common than chainmail or plate armor in Europe, lamellar armor played a significant role in certain historical periods and regions.
Leather Armor
Leather armor was commonly used during different periods of history, particularly by those who could not afford more expensive types of armor. It was typically made from layers of hardened or reinforced leather, offering some protection against cutting and impact. Leather armor was lightweight and allowed for greater mobility compared to heavier armors. While leather armor was not as effective as chainmail or plate armor, it still provided a level of protection against lower-impact attacks and was suitable for certain roles on the battlefield.
Each type of armor played a significant role in history, reflecting the advancements in warfare and the evolving needs of warriors. From the flexible and protective chainmail armor to the formidable plate armor, the variety of armor types allowed warriors to adapt to different combat situations. Understanding the features and significance of these armor types provides us with valuable insights into the military tactics and strategies employed during the medieval period.
